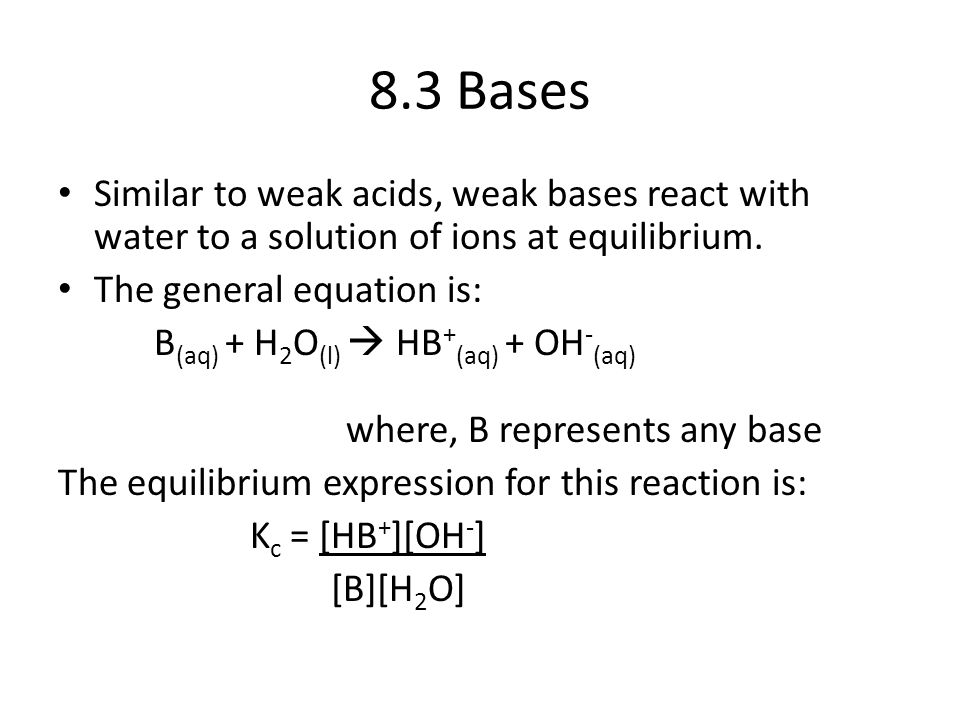
8.3 Bases Similar to weak acids, weak bases react with water to a
Price: $ 32.00
4.5(175)
Base Dissociation Constant, Kb Just as with weak acids, the concentration of water is almost constant in a solution of weak base. Therefore, we can group the constant terms in the equation. [H2O] Kc = [HB+][OH-] = Kb [B] Table 8.3 (Pg. 404 lists some common base dissociation constants, Kb).
8.3 Bases Similar to weak acids, weak bases react with water to a solution of ions at equilibrium. The general equation is: B(aq) + H2O(l) HB+(aq) +.
B(aq) + H2O(l) HB+(aq) + OH-(aq) where, B represents any base. The equilibrium expression for this reaction is: Kc = [HB+][OH-] [B][H2O].
Just as with weak acids, the concentration of water is almost constant in a solution of weak base. Therefore, we can group the constant terms in the equation. [H2O] Kc = [HB+][OH-] = Kb. [B] Table 8.3 (Pg. 404 lists some common base dissociation constants, Kb).
1. Write the balanced chemical equation. NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) Given: [NH3] = mol/L. 2. Set up an ICE table..
Change. -x. +x. Equilibrium x. Write the equation for the base dissociation constant, Kb. Kb =[NH4+][OH-] [NH3] From the table, Kb(NH3) = 1.8 x.
1.8 x 10-5 = (x) (x) (0.105 – x) Look at [NH3]/Kb. = 0.105/1.8x10-5 = 5833 > 100, so the amount of NH3 that dissociates is negligible compared to the initial [NH3] Therefore, (0.105 – x), becomes (0.105) solve for x..
6. Solve for pOH. pOH = -log[OH-] = -log[1.374 x 10-3] =.
Therefore, the pH of the ammonia solution is.
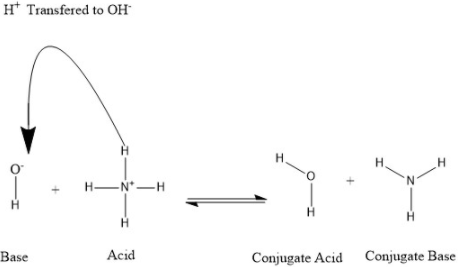
For any acid and its conjugate base. Ka(Kb) = [H3O+][OH-] = Kw. What does this mean The stronger an acid is, the weaker its conjugate base is. The conjugate of a strong acid is always a weak base. The conjugate of a strong base is always a weak acid..
A weak acid and its conjugate base. OR. A weak base and its conjugate acid. Buffer solutions resist a change in pH when a moderate amount of acid or base is added. Buffer solutions are made 2 ways: Use a weak acid and one of its salts. Eg. Mix acetic acid and sodium acetate. Use a weak base and one of its salts. Eg. Mix ammonia and ammonium chloride..
Sodium acetate is very soluble, so [CH3COO-] is high. Adding and acid or base has only a slight effect on pH because the H3O+ or OH- ions are removed by one of the components of the buffer solution..
For example: pH of arterial blood is ~7.4. It must stay b/n 7.0 and 7.5 or the organism may die. Blood is buffered by the equilibrium between CO3 ions and HCO3 ions. (formed by the reaction of dissolved CO2 and H2O).
= Graph of the pH of an acid (or base) against the volume of and added base (or acid) Titration reactions are used to find the equivalence point. Equivalence point – point where the acid and base completely react with one another. If, V1, V2 and C1 are known. C2 can be found (C1V1 = C2V2).
pH changes rapidly near the equivalence point. A single drop of titrant can change the pH by 2 pH units. The colour change indicates equivalence even if the colour change happens at pH of 8. As long as it is in the steep section of the curve. Strong acid titrated with strong base..
Weak acid titrated with strong base..
Is this the titration curve for a weak acid titrated with a strong base Explain.

Acid-Base Reactions strong acid + strong base strong acid + weak base weak acid + strong base weak acid + weak base. - ppt download

8.3.3 Distinguish between strong and weak acids and bases

8.4 Strong and weak acids and bases (SL)
Conjugate Acid Encyclopedia MDPI
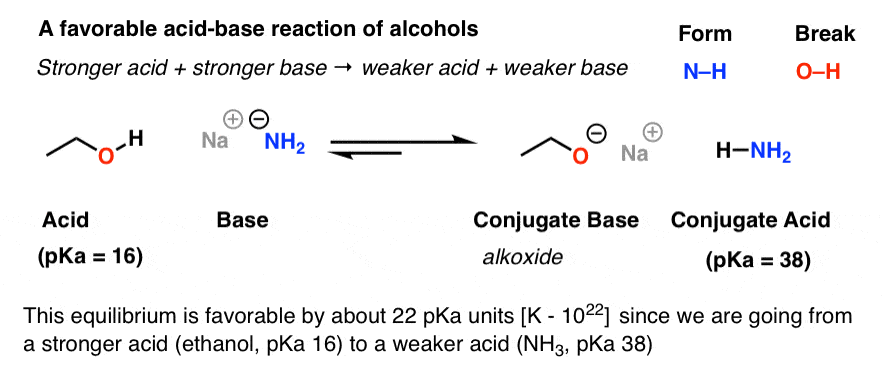
Acidity and Basicity of Alcohols – Master Organic Chemistry

Comparing Strong & Weak Acids (8.2.8), DP IB Chemistry: HL Revision Notes 2016

PPT - Topic 08 – Acids/Bases 8.3 – Strong and Weak Acids and Bases PowerPoint Presentation - ID:6273932

PPT - Weak and Strong Acids PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:2942157
8.3 Bases Similar to weak acids, weak bases react with water to a solution of ions at equilibrium. The general equation is: B(aq) + H2O(l) HB+(aq) + - ppt video online download
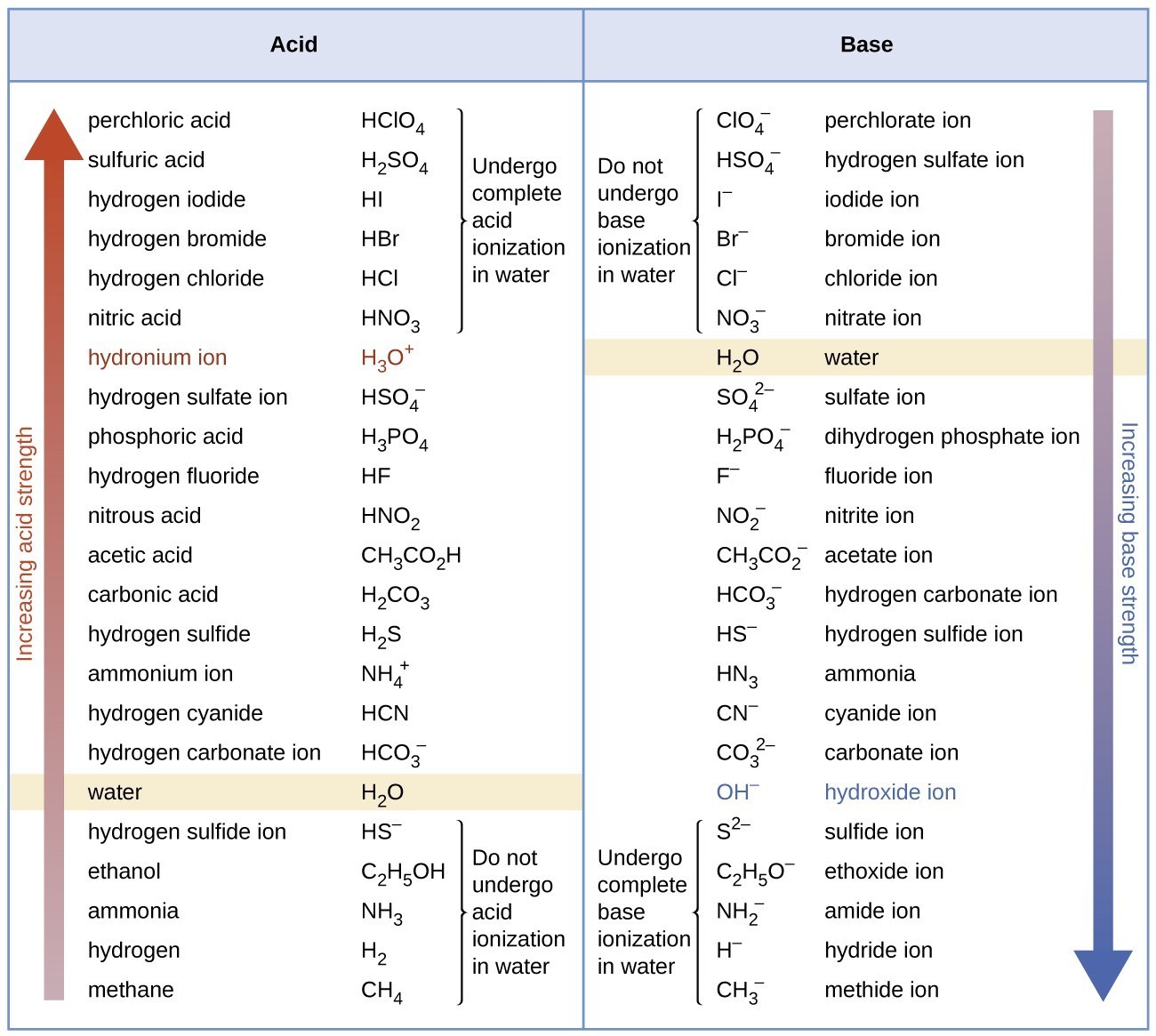
Relative Strengths of Acids and Bases




