Using the MO diagram of NO, calculate the bond order. Compare it to NO^(+)?
Price: $ 11.50
4.7(782)
The MO diagram for "NO" is as follows (Miessler et al., Answer Key): (The original was this; I added the orbital depictions and symmetry labels. For further discussion on the orbital energy ordering being "N"_2-like, see here and comments.) Quick overview of what the labels correspond to what MOs: 1a_1 is the sigma_(2s) bonding MO. 2a_1 is the sigma_(2s)^"*" antibonding MO. 1b_1 is the pi_(2p_x) bonding MO. 1b_2 is the pi_(2p_y) bonding MO. 3a_1 is the sigma_(2p_z) bonding MO, but it's relatively nonbonding with respect to oxygen. 2b_1 is the pi_(2p_x)^"*" antibonding MO. 2b_2 is the pi_(2p_y)^"*" antibonding MO. 4a_1 is the sigma_(2p_z)^"*" antibonding MO. To obtain the bond order, look at the molecular orbitals formed and decide whether they are bonding or antibonding. "BO" = 1/2 ("bonding e"^(-) - "antibonding e"^(-)) = 1/2[(2+2+2+2) - (2+1)] = color(blue)(2.5) And this should make sense because "NO"^(+) is isoelectronic with "CO", which has a bond order of 3. With one additional electron in an antibonding orbital (2b_2), the bond order decreases by 1/2 relative to "NO"^(+). If paramagnetism occurs due to unpaired electrons, is "NO" paramagnetic or diamagnetic?

Molecular Orbital Theory: Postulates, Types & Features
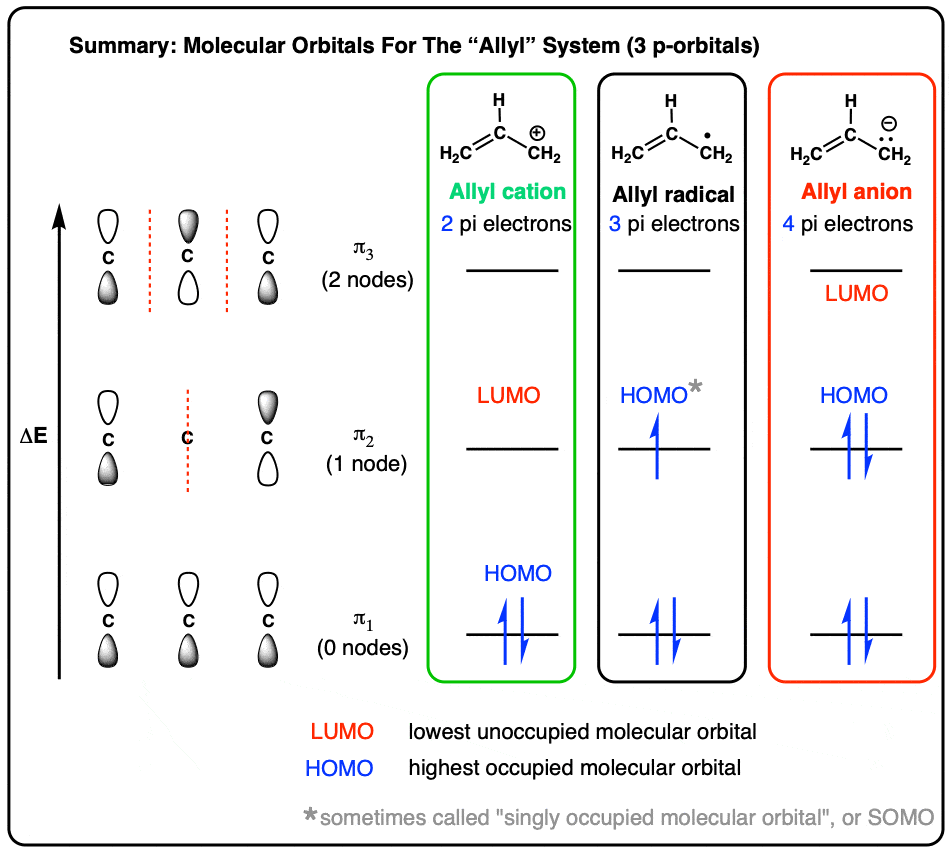
Molecular Orbitals of The Allyl Cation, Allyl Radical, and Allyl Anion

3 Ways to Calculate Bond Order in Chemistry - wikiHow

8.5 Molecular Orbital Theory
Consider the following molecules: NO, NO+ and NO-. Using the
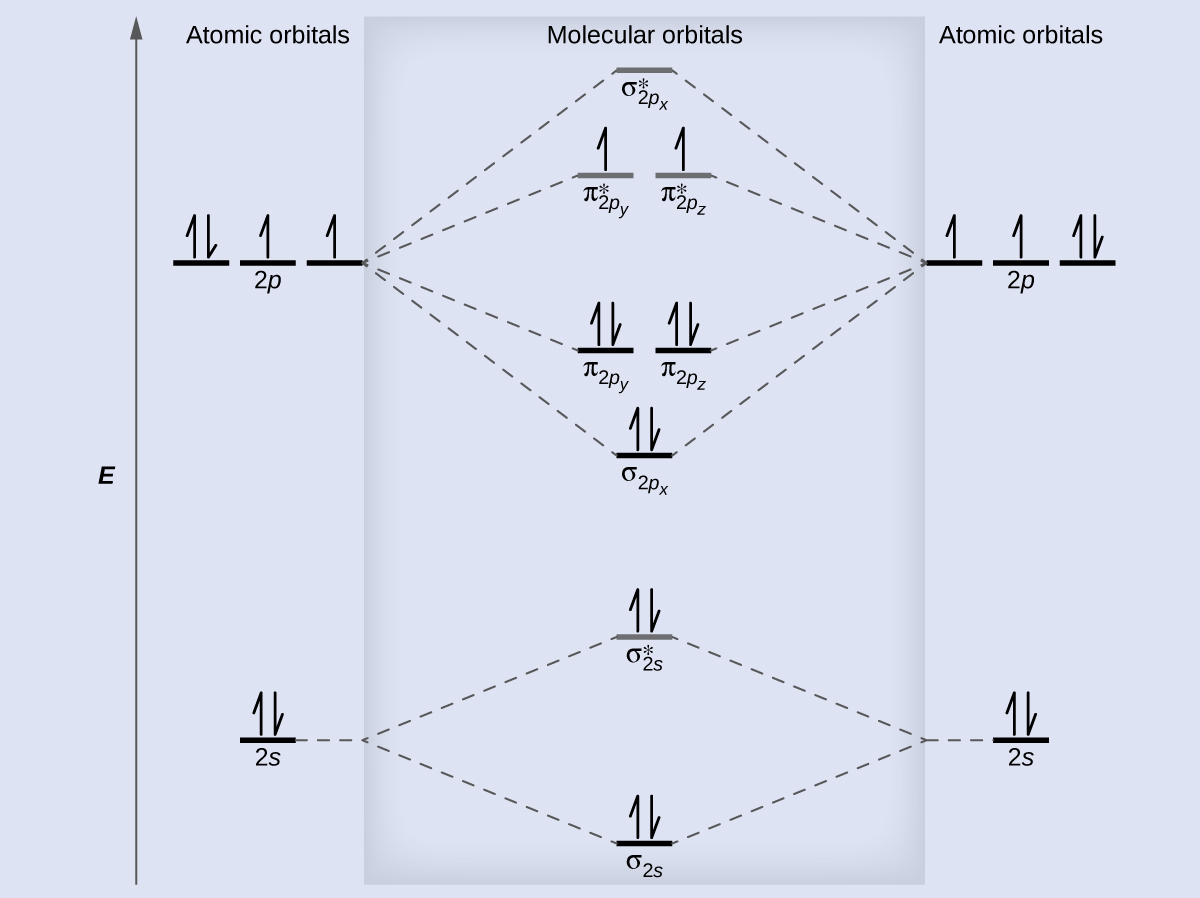
Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry
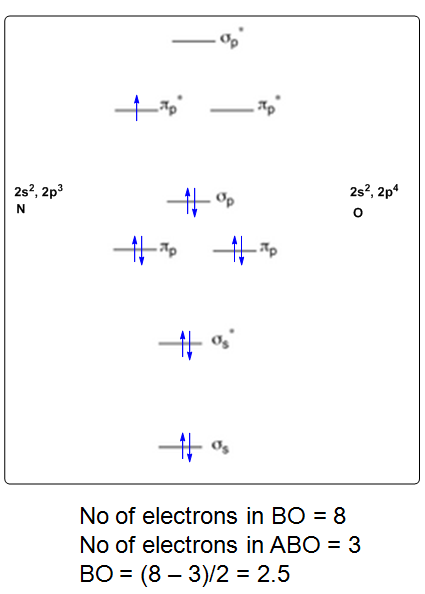
Answered: Use the MO diagram (below) to calculate…
Molecular Orbitals
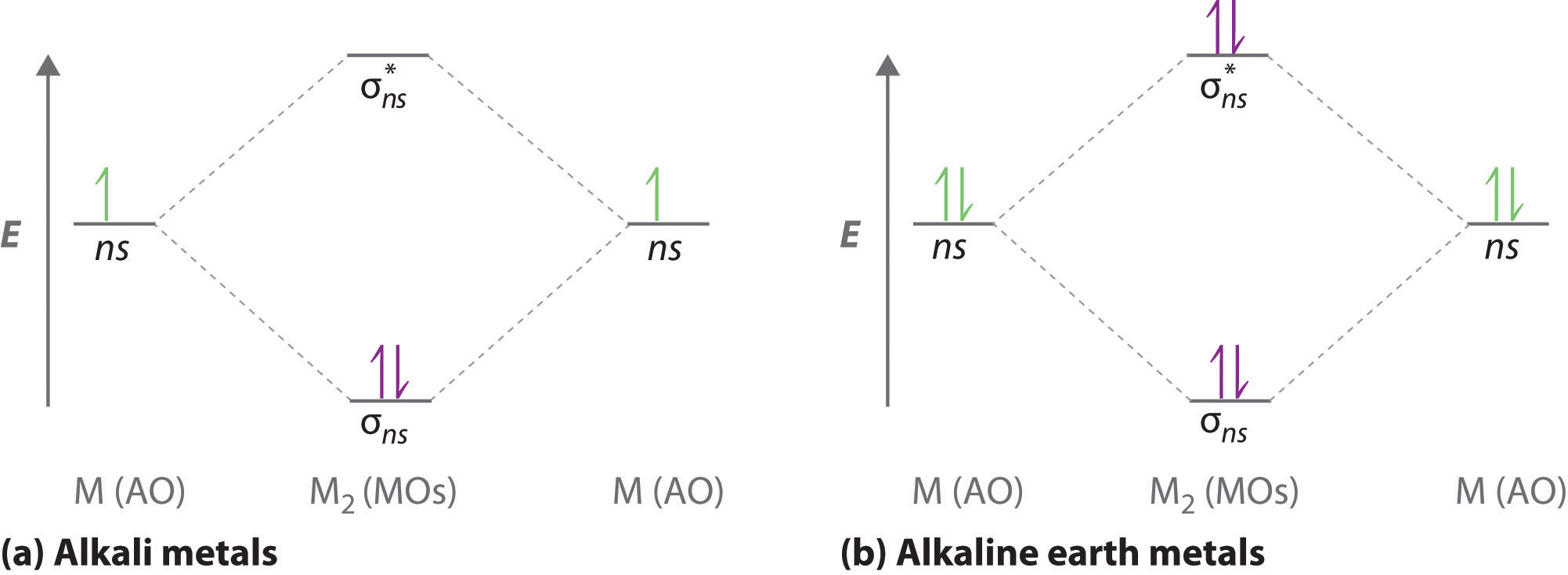
11.5: Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts
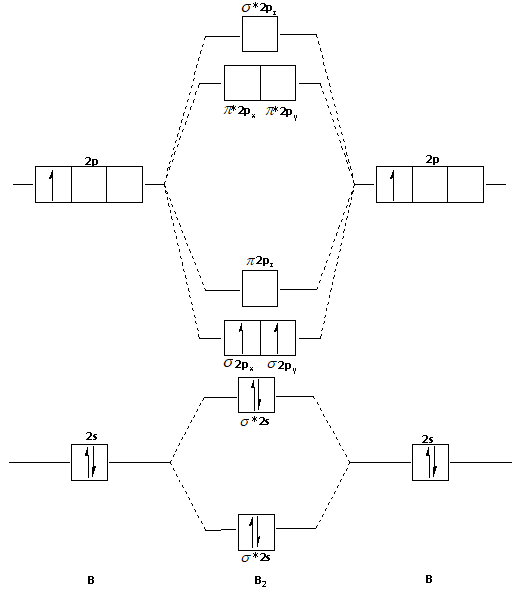
Draw MOT diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule and

Solved Use the blank MO diagram (below) to aid in answering




