Modulation of Cytochrome P450 Gene Expression and Arachidonic Acid Metabolism during Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in Rats
Price: $ 25.99
4.9(328)
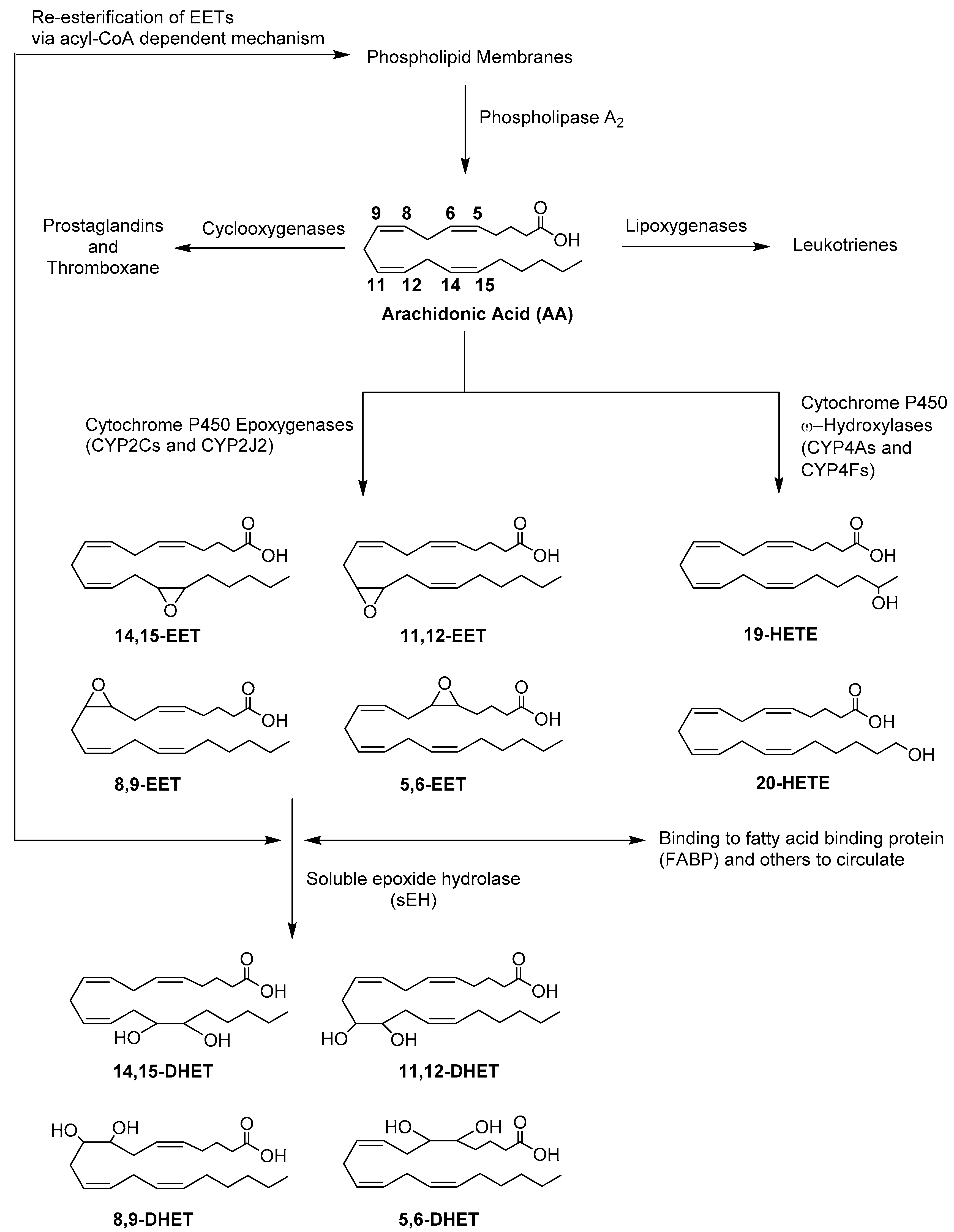
Several cytochrome P450 (P450) enzymes have been identified in the heart, and their levels have been reported to be altered during cardiac hypertrophy. Moreover, there is a strong correlation between P450-mediated arachidonic acid metabolites and the pathogenesis of cardiac hypertrophy. Therefore, we investigated the effect of isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy on the expression of several P450 genes and their associated P450-derived metabolites of arachidonic acid. Cardiac hypertrophy was induced by seven daily i.p. injections of 5 mg/kg isoproterenol. Thereafter, the heart, lung, liver, and kidney were harvested, and the expression of different genes was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Heart microsomal protein from control or isoproterenol treated rats was incubated with 50 μM arachidonic acid, and arachidonic acid metabolites were determined by liquid chromatography-electron spray ionization-mass spectrometry. Our results show that isoproterenol treatment significantly increased the heart/body weight ratio and the hypertrophic markers. In addition, there was a significant induction of CYP1A1, CYP1B1, CYP4A3, and soluble epoxide hydrolase and a significant inhibition of CYP2C11 and CYP2E1 in the hypertrophied hearts as compared with the control. CYP1A1, CYP2E1, and CYP4A3 gene expression was induced in the kidney, and CYP4A3 was induced in the liver of isoproterenol-treated rats. Isoproterenol treatment significantly reduced 5,6-, 8,9-, 11,12-, and 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid formation and significantly increased their corresponding 8,9-, and 14,15-dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid and the 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid metabolite. In conclusion, isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy alters arachidonic acid metabolism and its associated P450 enzymes, suggesting their role in the development and/or progression of cardiac hypertrophy.

Full article: Modulation of cardiac cytochrome P450 in patients with heart failure

Cytochrome P450 epoxygenase metabolite, 14,15-EET, protects against isoproterenol-induced cellular hypertrophy in H9c2 rat cell line - ScienceDirect
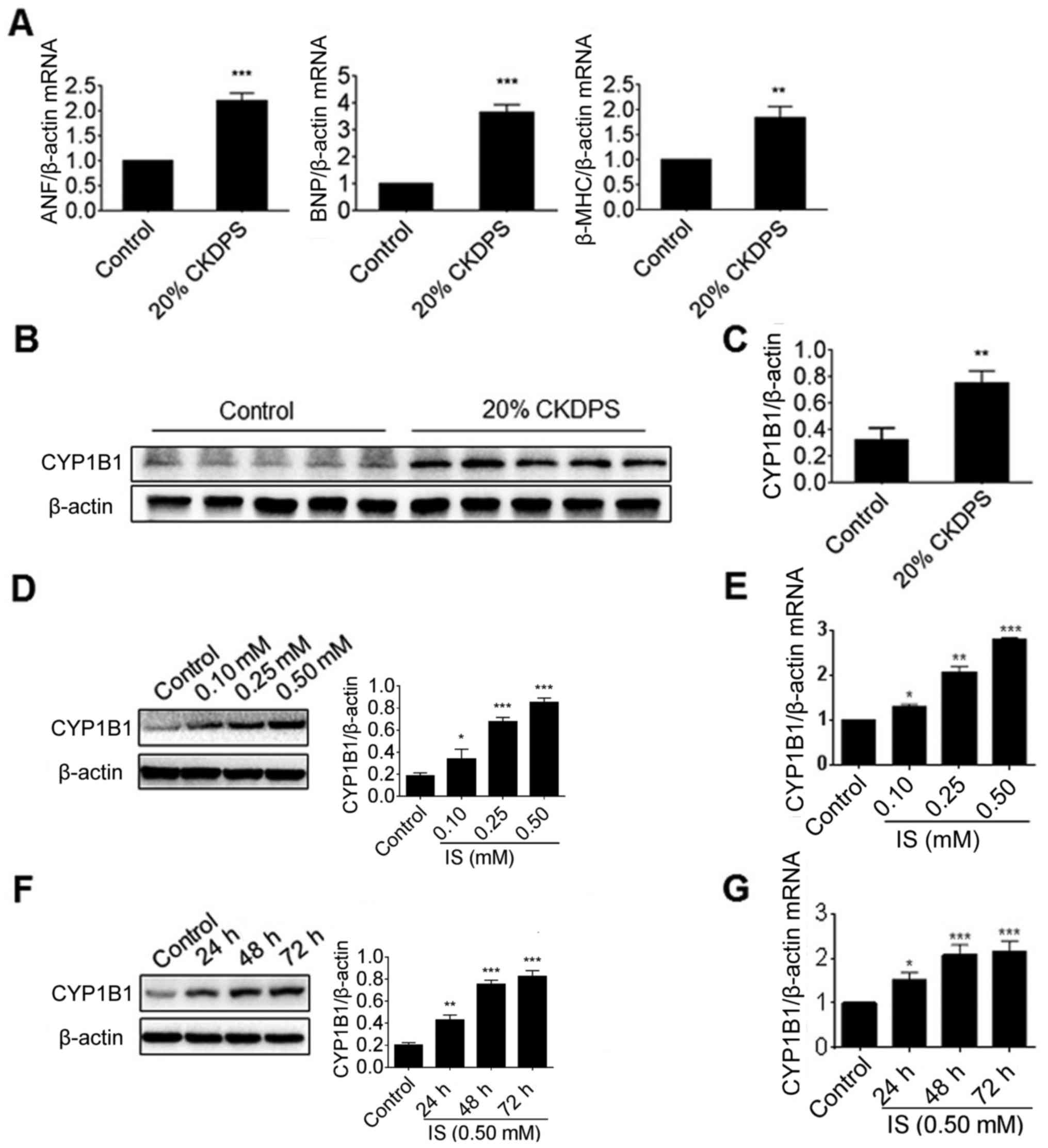
Inhibition of CYP1B1 ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy induced by uremic toxin

Metabolism pathways of arachidonic acids: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. - Abstract - Europe PMC
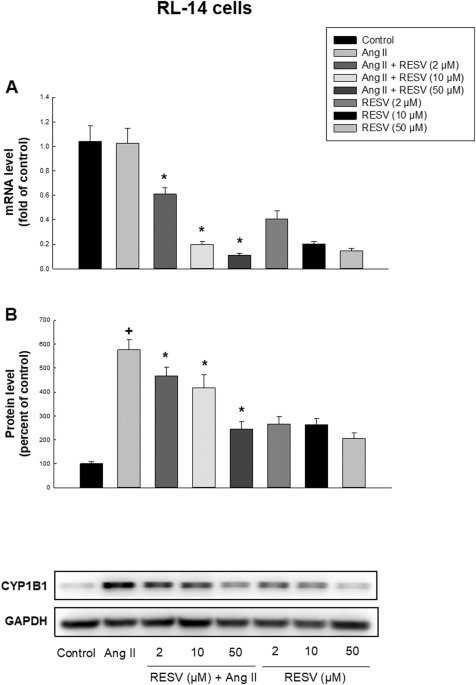
Resveratrol attenuates angiotensin II-induced cellular hypertrophy through the inhibition of CYP1B1 and the cardiotoxic mid-chain HETE metabolites
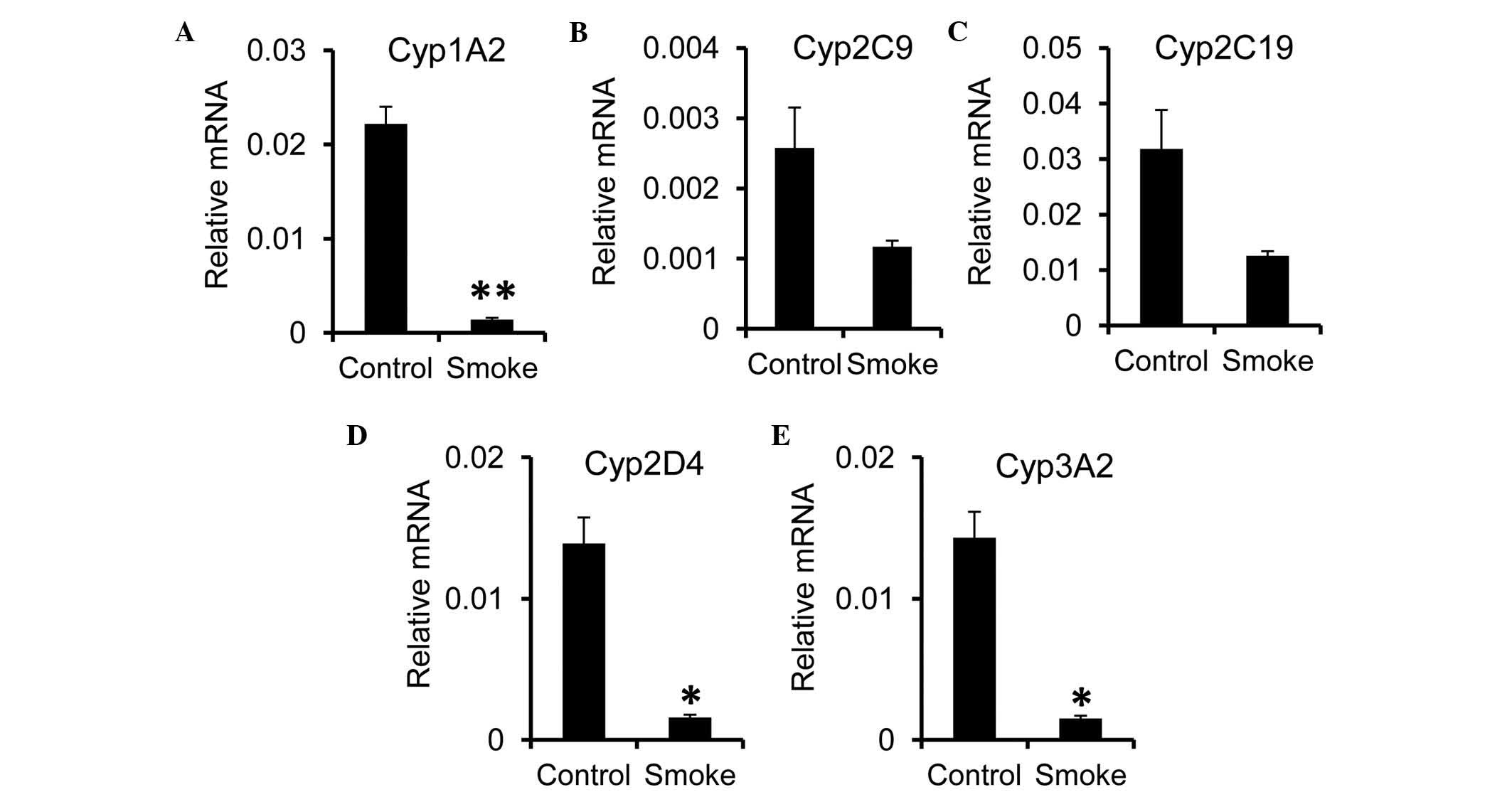
Glucocorticoid receptor contributes to the altered expression of hepatic cytochrome P450 upon cigarette smoking

Investigating the relevance of CYP2J2 inhibition for drugs known to cause intermediate to high risk torsades de pointes - ScienceDirect
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Cytochrome P450 2J2: Potential Role in Drug Metabolism and Cardiotoxicity

Cytochrome P450 and Vascular Homeostasis

PDF] Cytochrome P450 and arachidonic acid metabolites: role in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury revisited.




